Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the respiratory and digestive systems. It results in the production of thick and sticky mucus that can clog airways and disrupt the normal functioning of organs. Advances in medicine have improved life expectancy for individuals with CF, yet it remains a challenging condition requiring lifelong management.
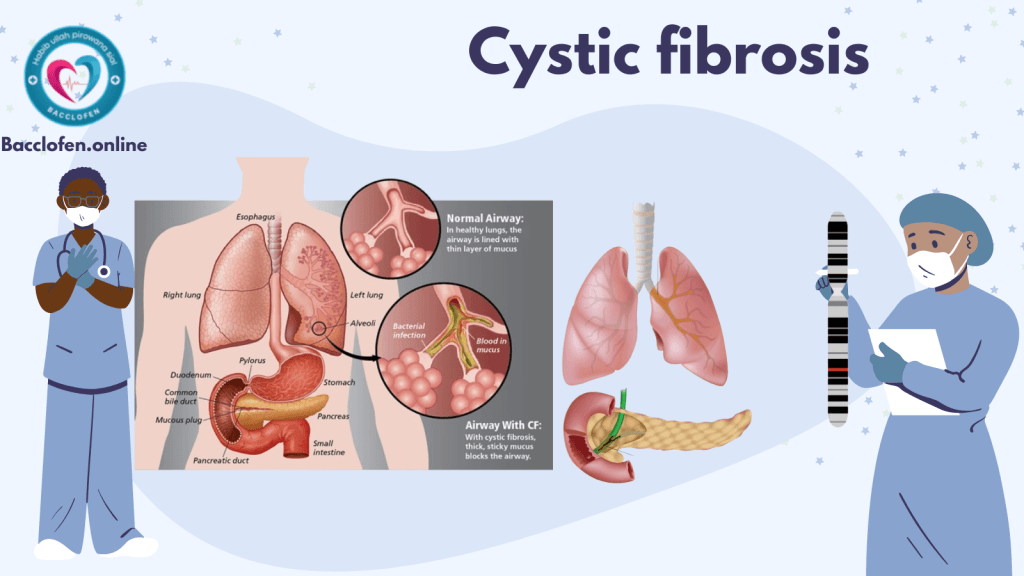
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) gene. This gene regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells. Mutations lead to the production of a faulty protein, resulting in thick mucus buildup in the lungs, pancreas, and other organs.
Genetics and Inheritance
- Recessive Inheritance:
CF is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning a child must inherit a defective CFTR gene from both parents to develop the disease. - Carriers:
Individuals with only one copy of the defective gene are carriers and typically do not show symptoms.
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
CF symptoms vary in severity and may differ between individuals, even within the same family. The most commonly affected systems are the respiratory and digestive tracts.
Respiratory Symptoms
- Chronic cough with thick mucus.
- Repeated lung infections, including bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Wheezing and shortness of breath.
- Nasal congestion and sinus infections.
Digestive Symptoms
- Poor weight gain and growth, despite a healthy appetite.
- Greasy, bulky stools due to poor fat absorption.
- Intestinal blockages, particularly in newborns (meconium ileus).
- Pancreatic enzyme deficiencies, leading to malnutrition.
Other Symptoms
- Salty-tasting skin.
- Diabetes due to damage to the pancreas.
- Liver disease caused by bile duct blockages.
- Infertility, particularly in males.
Complications of Cystic Fibrosis
Without proper management, CF can lead to severe complications, including:
- Respiratory Failure: Chronic lung damage can eventually impair breathing.
- Diabetes: Cystic fibrosis-related diabetes (CFRD) occurs due to pancreatic damage.
- Osteoporosis: Malnutrition and chronic inflammation can weaken bones.
- Liver Disease: Scarring of the liver may occur due to bile buildup.
Prevention of Cystic Fibrosis
As a genetic disorder, CF cannot be prevented after conception. However, steps can be taken to reduce the risk of passing it to offspring:
1. Genetic Counseling
Couples with a family history of CF or known carriers of the CFTR gene mutation should consider genetic counseling. Testing can determine the likelihood of passing CF to their children.
2. Prenatal Testing
If both parents are carriers, prenatal testing like chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis can detect CF in the developing fetus.
Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
Early and accurate diagnosis is critical for effective management. CF can be diagnosed through a combination of tests:
1. Newborn Screening
- Many countries include CF in routine newborn screening programs.
- Blood tests measure levels of immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT), an enzyme elevated in CF.
2. Sweat Test
- The gold standard for CF diagnosis.
- Measures the salt content in sweat. High levels indicate CF.
3. Genetic Testing
- Identifies mutations in the CFTR gene.
- Used for confirming a diagnosis or testing family members.
4. Pulmonary Function Tests
- Evaluates lung function by measuring airflow and lung capacity.
Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
While there is no cure for CF, treatments focus on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
1. Airway Clearance Techniques (ACTs)
- Methods like chest physiotherapy, vibration vests, or postural drainage help loosen and expel mucus from the lungs.
2. Medications
- Bronchodilators: Open airways to ease breathing.
- Mucolytics: Thin mucus to make it easier to clear.
- Antibiotics: Treat and prevent lung infections.
- CFTR Modulators: Address the underlying cause of CF by improving the function of the faulty CFTR protein. Examples include ivacaftor, lumacaftor, and tezacaftor.
3. Nutritional Support
- High-calorie, nutrient-rich diets to address malabsorption.
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements to aid digestion.
- Vitamin and mineral supplements, particularly fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K).
4. Lung Transplant
- Considered in advanced cases where lung function is severely compromised.
5. Management of Complications
- Diabetes: Insulin therapy and blood sugar monitoring.
- Liver Disease: Medications to improve bile flow and prevent liver damage.
Living with Cystic Fibrosis
Advances in CF care have significantly improved life expectancy and quality of life. Managing CF involves a multidisciplinary approach with a healthcare team, including pulmonologists, dietitians, and physical therapists.
Lifestyle Tips for Better Management
- Regular Exercise: Improves lung function and overall health.
- Avoiding Smoke and Pollutants: Protects the lungs from additional damage.
- Staying Up to Date with Vaccinations: Reduces the risk of respiratory infections.
Global Impact and Research
CF affects approximately 70,000 people worldwide, predominantly those of European descent. Ongoing research focuses on:
- Developing advanced CFTR modulators.
- Exploring gene therapy to correct or replace the defective CFTR gene.
- Enhancing diagnostic and treatment options.
Also check
Inspiring story there. What occurred after? Thanks!
It’s actually a nice and helpful piece of information.
I’m happy that you simply shared this helpful information with us.
Please stay us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I do believe all of the ideas you’ve offered for your post.
They are really convincing and can definitely work.
Still, the posts are very brief for novices. Could you
please lengthen them a little from next time? Thanks for
the post.
Hello everyone, it’s my first go to see at
this site, and article is in fact fruitful in favor of me, keep up posting such articles.
Stunning story there. What happened after? Thanks!
I feel this is one of the so much significant information for me.
And i am satisfied studying your article. However should observation on few normal things,
The website taste is ideal, the articles is really great :
D. Excellent activity, cheers
I was able to find good info from your blog posts.
Pingback: Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment - Bacclofen
Asking questions are in fact good thing if you are not understanding anything totally,
except this post gives fastidious understanding even.
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really useful
& it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and aid others like
you aided me.