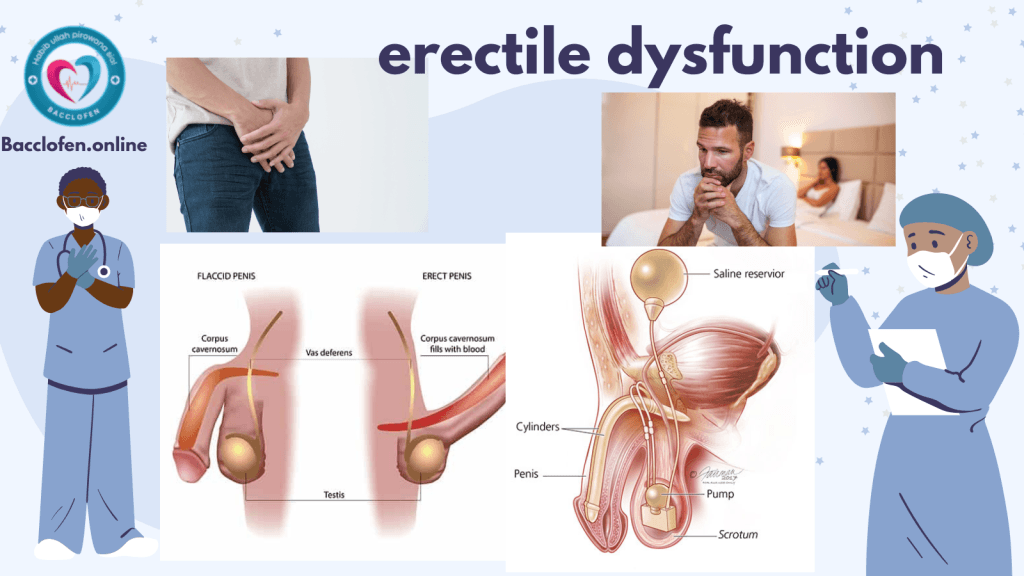
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It is characterized by the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. While occasional difficulties with erections are normal and can occur due to stress or fatigue, persistent ED may indicate underlying health issues or psychological concerns that require attention.
Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction can arise from a variety of factors, often categorized into physical, psychological, or lifestyle-related causes. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective treatment and management.
1. Physical Causes
Physical health issues are among the most common causes of ED. These include:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Conditions such as atherosclerosis (narrowing of blood vessels) can reduce blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve an erection.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and blood vessels, leading to ED.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Low testosterone levels or other hormonal disorders can impact sexual function.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions like Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries can interfere with nerve signals required for erections.
- Chronic Kidney or Liver Disease: These conditions can affect overall health and sexual function.
- Medications: Certain drugs, such as antidepressants, blood pressure medications, and chemotherapy agents, can contribute to ED.
2. Psychological Causes
Mental health plays a significant role in sexual function. Psychological causes of ED include:
- Stress: Work-related stress or personal life pressures can affect sexual performance.
- Anxiety: Performance anxiety or general anxiety disorders can interfere with the ability to maintain an erection.
- Depression: Low mood and loss of interest in pleasurable activities, including sex, are common in individuals with depression.
- Relationship Issues: Conflicts or lack of intimacy in a relationship can lead to ED.
3. Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can also contribute to ED:
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and restricts blood flow to the penis.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Impairs the nervous system and can lead to temporary or long-term ED.
- Obesity: Associated with hormonal imbalances and reduced cardiovascular health, both of which can lead to ED.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary behavior contributes to poor circulation and overall health.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
The primary symptom of ED is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual activity. Other associated symptoms may include:
- Reduced sexual desire or libido.
- Difficulty achieving an erection even with stimulation.
- Inconsistent erections that are not firm enough for penetration.
- Emotional distress, anxiety, or embarrassment related to sexual performance.
Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
Diagnosing ED involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and specialized tests. Key steps in the diagnostic process include:
- Medical History: A detailed discussion of symptoms, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions helps identify potential causes.
- Physical Examination: A doctor may examine the penis, testicles, and check for signs of hormonal or vascular issues.
- Blood Tests: Used to identify conditions like diabetes, low testosterone, or high cholesterol.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound or other imaging techniques can assess blood flow to the penis.
- Psychological Assessment: A mental health evaluation may be recommended if psychological factors are suspected.
Treatment Options for Erectile Dysfunction
The treatment of ED depends on the underlying cause and can involve a combination of medical, psychological, and lifestyle interventions.
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Making positive changes in lifestyle can significantly improve ED. These include:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and overall health.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports vascular health.
- Quitting Smoking and Alcohol: Eliminating these habits can improve blood flow and nerve function.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of ED.
2. Medications
Several medications are available to treat ED effectively. These include:
- Phosphodiesterase Type 5 (PDE5) Inhibitors: Drugs like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) enhance blood flow to the penis. These are often the first line of treatment.
- Hormone Therapy: Testosterone replacement therapy may be prescribed if low testosterone levels are detected.
- Injectable Medications: Alprostadil can be injected directly into the penis to promote an erection.
3. Psychological Counseling
For ED with psychological causes, counseling or therapy can be highly effective. Options include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps address anxiety or negative thought patterns related to sexual performance.
- Couples Therapy: Improves communication and intimacy between partners, addressing relationship issues that may contribute to ED.
4. Medical Devices and Procedures
For individuals who do not respond to medications, the following options may be considered:
- Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs): These devices create a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into it to achieve an erection.
- Penile Implants: Surgical implantation of devices that can be manually inflated to create an erection.
- Vascular Surgery: In rare cases, surgery to repair damaged blood vessels may be performed.
Prevention of Erectile Dysfunction
While some causes of ED cannot be prevented, adopting healthy habits can reduce the risk:
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Monitor and manage conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cholesterol.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, to reduce stress levels.
- Open Communication: Discuss sexual health openly with your partner and seek professional help when needed.
Conclusion
Erectile dysfunction is a common yet treatable condition that affects the quality of life for many individuals. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, those affected can take proactive steps toward improvement. Whether through lifestyle changes, medications, or counseling, seeking help for ED is an essential step toward restoring confidence, intimacy, and overall well-being. Always consult a healthcare professional for a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment.