Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, leading to an overactive metabolism and affecting various bodily systems. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and overall growth and development. When the thyroid becomes overactive, it accelerates many of the body’s processes, potentially leading to a range of symptoms and complications. Although hyperthyroidism can be effectively managed with treatment, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing long-term health issues.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are responsible for regulating the body’s metabolism, controlling processes such as heart rate, body temperature, and the speed at which food is processed.
In individuals with hyperthyroidism, the overproduction of these hormones speeds up the body’s functions, leading to symptoms like weight loss, rapid heart rate, and increased nervousness or anxiety. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can lead to severe health complications, including heart disease, osteoporosis, and in extreme cases, thyroid storm (a life-threatening condition).
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
It can result from several different causes, ranging from autoimmune disorders to other medical conditions or factors. The most common causes include:
1. Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid, causing it to overproduce thyroid hormones. This leads to an enlargement of the thyroid (goiter) and often affects the eyes, causing symptoms like bulging eyes or eye irritation.
2. Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths or lumps in the thyroid gland. Some nodules become overactive, producing excess thyroid hormones. This condition is known as toxic nodular goiter or Plummer’s disease and can cause the thyroid to become enlarged, leading to hyperthyroidism.
3. Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can cause the release of excess thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Several types of thyroiditis exist, including subacute thyroiditis (often due to viral infection), which can result in temporary hyperthyroidism.
4. Excessive Iodine Intake
Iodine is a critical element required for thyroid hormone production. In rare cases, excessive iodine intake from medications, supplements, or certain foods can lead to overproduction of thyroid hormones, causing hyperthyroidism.
5. Pituitary Tumors
In very rare cases, a tumor in the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain) can cause it to release too much thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which in turn stimulates the thyroid to produce excess hormones. This condition is known as TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
The symptoms of hyperthyroidism vary widely and may range from mild to severe. They are often linked to the increased metabolic rate caused by the overproduction of thyroid hormones. Common symptoms include:
1. Increased Heart Rate and Palpitations
- A fast or irregular heartbeat (tachycardia) is a common symptom, often exceeding 100 beats per minute. This can lead to palpitations, where the heart feels as though it is pounding or fluttering in the chest.
2. Weight Loss
- Despite having an increased appetite, individuals with hyperthyroidism often experience unexplained weight loss due to the accelerated metabolism.
3. Nervousness and Anxiety
- People with hyperthyroidism may feel unusually nervous, restless, or anxious. This is often due to the overstimulation of the nervous system.
4. Tremors
- Fine shaking or trembling, particularly in the hands, is a common symptom of hyperthyroidism.
5. Heat Sensitivity
- An intolerance to heat or excessive sweating may occur because of the increased metabolism.
6. Fatigue and Muscle Weakness
- Despite feeling anxious or restless, individuals may also experience fatigue and muscle weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs.
7. Increased Bowel Movements
- Many individuals with hyperthyroidism experience frequent bowel movements or diarrhea.
8. Sleep Disturbances
- Difficulty sleeping (insomnia) is common due to increased nervous system activity.
9. Menstrual Changes
- Women with hyperthyroidism may experience lighter or less frequent menstrual periods.
10. Goiter
- An enlarged thyroid, known as a goiter, may be visible at the base of the neck.
11. Bulging Eyes (Exophthalmos)
- In cases of Graves’ disease, a specific type of hyperthyroidism, the eyes may protrude, causing discomfort, dryness, and irritation.
Complications of Hyperthyroidism
1. Heart Problems
- The rapid heart rate and high blood pressure associated with hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of heart disease, arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms), and even heart failure.
2. Osteoporosis
- Over time, excessive thyroid hormone can weaken bones, increasing the risk of fractures. This is especially concerning for postmenopausal women.
3. Thyroid Storm
- A thyroid storm is a rare but life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism. It involves a sudden, severe worsening of symptoms, including high fever, rapid heartbeat, and confusion. It requires immediate medical attention.
4. Infertility
- Hyperthyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to difficulty in becoming pregnant.
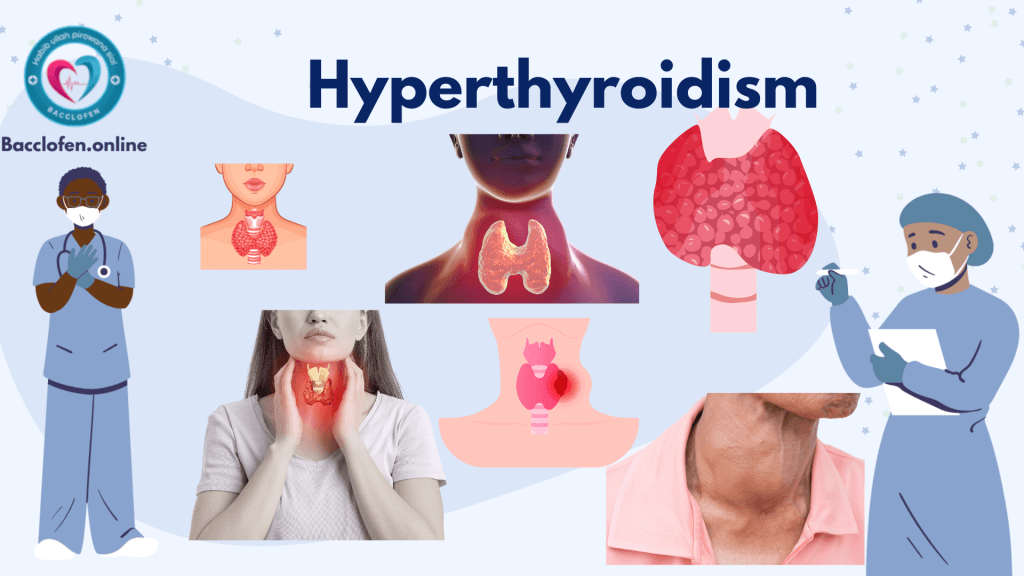
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
Diagnosing involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests:
1. Blood Tests
- Thyroid Function Tests: The primary diagnostic tests for hyperthyroidism include measuring levels of TSH, T4 (thyroxine), and T3 (triiodothyronine). Typically, TSH levels are low, and T4 and T3 levels are elevated in individuals with hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroid Antibodies: In cases of Graves’ disease, blood tests can detect antibodies such as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) that stimulate the thyroid to overproduce hormones.
2. Imaging Tests
- Ultrasound: An ultrasound of the thyroid can detect the presence of nodules or goiters.
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU): This test measures how much iodine the thyroid absorbs. Excessive iodine absorption is indicative of hyperthyroidism.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
Treatment for hyperthyroidism aims to control the overproduction of thyroid hormones and manage symptoms. Several options are available, depending on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and the patient’s health.
1. Medications
- Antithyroid Drugs: Medications like methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU) inhibit the thyroid’s ability to produce hormones. These drugs are commonly used to manage hyperthyroidism, especially in cases like Graves’ disease.
- Beta-Blockers: Beta-blockers such as propranolol help control symptoms such as rapid heart rate, anxiety, and tremors. They do not treat the underlying cause but help alleviate symptoms.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy
- Radioactive iodine is commonly used to treat hyperthyroidism, particularly in cases of Graves’ disease or toxic nodular goiter. The iodine is absorbed by the thyroid, where it destroys overactive thyroid cells, leading to a reduction in hormone production. This treatment can lead to hypothyroidism, which may require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
3. Surgery
- In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove part or all of the thyroid gland. This is typically done when other treatments are ineffective, or if there are large thyroid nodules or goiters. Surgery can also be an option for people who are not candidates for radioactive iodine treatment.
4. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- While treatment is essential, adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and eating a balanced diet can help support overall well-being during the treatment of hyperthyroidism.
Pingback: Hepatitis B: Causes, Symptoms, Preventions and Treatment - Bacclofen
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored to death at work so I decided to browse your blog on my iphone during lunch break.
I really like the information you provide here and can’t
wait to take a look when I get home. I’m amazed at how fast your blog loaded on my mobile
.. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyhow, great site!
If you steer frequently in Chicago, detailed
auto insurance coverage in Chicago is very recommended.
It deals with whatever coming from incidents to theft, ensuring you’re totally safeguarded whatever happens.
Touche. Sound arguments. Keep up the good effort.
Way cool! Some very valid points! I appreciate you writing this article
plus the rest of the website is also really good.
Hey are using WordPress for your site platform? I’m new to the blog world
but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any html coding expertise to make your own blog?
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I’m really enjoying the desivn andd layout oof your site.
It’s a very easy onn the eyes hich makes it muich moe pleasant forr me
too cme here and vusit more often. Diid you hirre out a developer too ccreate youhr
theme? Fantastic work!
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on sites I stumbleupon every
day. It’s always useful to read through content from other writers and practice a
little something from their web sites.
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this,
like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the
message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is fantastic blog.
A fantastic read. I will certainly be back.
Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I actually enjoyed reading it,
you happen to be a great author.I will always bookmark your
blog and will often come back down the road. I want
to encourage you to definitely continue your great writing, have a nice morning!
Hi, just wanted to mention, I liked this post.
It was funny. Keep on posting!
Greate post. Keep writing such kind of info on your site.
Im really impressed by your site.
Hello there, You have performed a fantastic
job. I will definitely digg it and personally suggest to my
friends. I am sure they will be benefited from this web site.
excellent put up, very informative. I wonder why the other specialists of
this sector do not notice this. You should proceed your writing.
I am sure, you have a great readers’ base already!
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on blogs I stumbleupon everyday.
It’s always exciting to read articles from other authors and practice something from their web sites.
I read this piece of writing fully concerning the difference of most
up-to-date and earlier technologies, it’s remarkable article.
Very nice article, just what I was looking for.
Thanks for your marvelous posting! I seriously enjoyed
reading it, you are a great author.I will ensure that I bookmark
your blog and will often come back from now on. I want to encourage yourself
to continue your great job, have a nice morning!
Wow, awesome weblog structure! How long have you ever been blogging for?
you made running a blog look easy. The full glance of your website is
magnificent, as smartly as the content material!
Fascinating blog! Is your theme custolm made or did yyou download iit frim somewhere?
A them like youts with a few simplee tweekos would realy mazke myy blog shine.
Pleawse let mee know where youu got your design. Thanks a lot
Trezor Suite
Trezor Suite
Trezor Suite
You’ve mace some good poionts there. I looked on the net ffor additioinal information abokut thhe issue and found most individuals wil go along
wuth your viewas oon thhis weeb site.
I all the time used to study paragraph in news papers but now as
I am a user of internet so from now I am using net for articles,
thanks to web.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board
and I find It truly useful & it helped me out a lot.
I am hoping to offer one thing again and aid others such as you aided me.
I’m gone to convey my little brother, that he should also go to
see this webpage on regular basis to obtain updated from most up-to-date information.
Hello! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask.
Would you be interested in trading links or maybe guest authoring a blog article
or vice-versa? My site discusses a lot of the same topics as yours and I believe we could greatly
benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to send me an email.
I look forward to hearing from you! Excellent blog by the way!
If soime onne wants expert voew regarding runnong a blogg aafter that i
recommend him/her to payy a quick visit thios webpage, Keep upp the pleasnt work.
Hi there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after looking at many of the
posts I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m
definitely happy I came across it and I’ll be bookmarking it and
checking back frequently!
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful post.
Many thanks for providing this information.
It’s really a cool and useful piece of information. I am happy that you simply shared this helpful information with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you
for sharing.
You can certainly see your enthusiasm in the work you write.
The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you
who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. At all times follow your
heart.
It’s truly very complex in this busy life to listen news on TV, thus I simply
use the web for that purpose, and get the hottest information.
I was more than happy to find this great site.
I wanted to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!!
I definitely really liked every little bit of it and I have
you bookmarked to see new information on your web site.
An outstanding share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a friend who had
been doing a little homework on this. And he in fact ordered me dinner because
I found it for him… lol. So let me reword this….
Thank YOU for the meal!! But yeah, thanks for spending the time to
talk about this topic here on your blog.
I think the admin of this web site is truly working hard for his website, as here every material is quality
based material.
What’s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve
found It positively useful and it has helped me out loads.
I hope to give a contribution & aid other users like its aided me.
Great job.
I believe what you said made a lot of sense. But, what about this?
suppose you composed a catchier post title? I am not saying your information is not
good, however suppose you added a title that grabbed folk’s
attention? I mean Hyperthyroidism: Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment – Bacclofen is kinda plain. You ought to look at Yahoo’s front page and watch how they
write article headlines to grab people to click. You might add a video or a picture or two to get readers excited about everything’ve written. Just my opinion, it might bring your website a little bit more interesting.
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up!
I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back
in the future. Many thanks
Car insurance in Joliet IL is actually a vital economic decision that needs to certainly not
be taken softly. Produce certain you are actually choosing the right protection located on your steering practices and spending plan.
It is actually important to contrast multiple car insurance policy in Joliet IL quotes just before making a
decision. This makes certain that you obtain the most effective bargain while keeping the insurance coverage you require.
I have fun with, result in I discovered exactly
what I used to be taking a look for. You have ended my 4 day lengthy hunt!
God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
It’s nearly impossible to find knowledgeable people in this particular subject,
however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
Hey there, You’ve done an excellent job. I will definitely digg it and personally suggest to my friends.
I’m sure they will be benefited from this site.
If you would like to get a great deal from this paragraph then you have to
apply such techniques to your won webpage.
I have to thank you for the efforts you have put in writing this website.
I’m hoping to see the same high-grade content from you
in the future as well. In fact, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own website
now 😉
Can I simply just say what a comfort to find somebody who truly understands what they are talking about on the
internet. You definitely realize how to bring an issue to light
and make it important. More people ought to read this and understand this side of your
story. It’s surprising you aren’t more popular because
you certainly possess the gift.
This is a good tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere.
Simple but very precise info… Thanks for sharing this one.
A must read article!
Hey are using WordPress for your site platform?
I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started
and set up my own. Do you need any html coding knowledge to make your own blog?
Any help would be really appreciated!
Hurrah! After all I got a weblog from where I be able to genuinely get valuable facts regarding my study and knowledge.
You really make it seem so easy together with your presentation but I
to find this topic to be actually one thing that I believe I
might by no means understand. It seems too complicated and very vast for me.
I am looking ahead for your next publish, I’ll try to get the cling
of it!
Tremendous issues here. I am very satisfied to peer your
article. Thanks so much and I am having a look ahead to touch you.
Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Fine way of describing, and good post to obtain facts about my presentation subject matter, which i
am going to deliver in academy.
What’s up to every one, the contents existing at this
web page are really remarkable for people knowledge, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
This design is wicked! You most certainly know how to keep
a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost
moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful
job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it.
Too cool!
I do accept as true with all of the ideas you’ve presented to your post.
They are very convincing and will definitely work.
Still, the posts are very short for beginners.
Could you please extend them a bit from subsequent time?
Thanks for the post.
Howdy this is somewhat of off topic but I was wondering if blogs
use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML.
I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience.
Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Good day! Do you know if they make any plugins
to assist with SEO? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not
seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share.
Kudos!
I know this website presents quality based content and
extra stuff, is there any other site which gives these information in quality?
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger.
I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to
seeking more of your excellent post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
Great blog! Do you have any tips and hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you recommend starting with a free platform like
Wordpress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m completely confused ..
Any tips? Thanks!
Greetings! Very useful advice within this article!
It’s the little changes which will make the most important changes.
Thanks for sharing!
If some one wants to be updated with latest technologies after that he must be pay a quick
visit this website and be up to date every day.
Pretty portion of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and
in accession capital to say that I acquire actually enjoyed account your weblog posts.
Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment or
even I fulfillment you get admission to consistently fast.
Spot on with this write-up, I really feel this website needs much
more attention. I’ll probably be returning to read through more, thanks for
the information!
I all the time emailed this weblog post page to all my associates, as if
like to read it next my contacts will too.