Menstruation is a crucial aspect of human biology, marking the shedding of the uterine lining in individuals with a uterus. It is part of the menstrual cycle, a complex physiological process regulated by hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. Menstruation typically begins during adolescence and continues until menopause, with the average age of onset being around 12-13 years, although it can vary. The menstrual cycle typically lasts 28 days, though some may have cycles that are shorter or longer, with menstruation itself lasting between 3 and 7 days.
During menstruation, the body sheds the thickened lining of the uterus, which was prepared to receive a fertilized egg. If fertilization does not occur, this lining, along with blood and other fluids, is expelled from the body through the vagina. Menstruation serves as an indicator of the body’s reproductive health and fertility.
Common Menstrual Disorders
While menstruation is a natural process, many individuals experience menstrual disorders that can impact their daily lives. These disorders vary in severity and can manifest as irregularities, pain, or excessive bleeding. Below are some of the most common menstrual disorders.
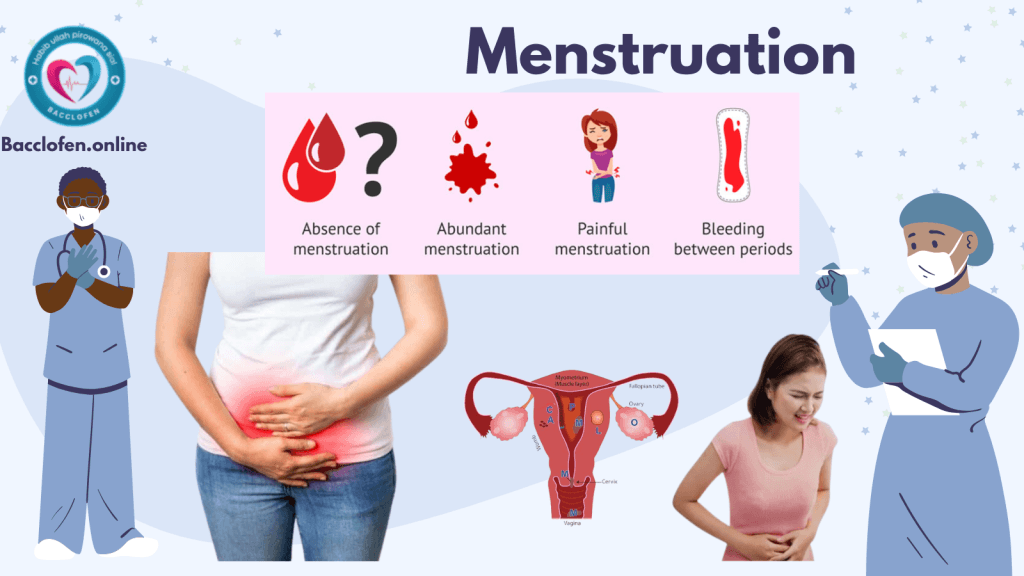
1. Dysmenorrhea (Painful Menstruation)
Dysmenorrhea refers to painful menstruation, which is one of the most commonly reported menstrual disorders. The pain typically occurs in the lower abdomen or pelvis and may be accompanied by nausea, headaches, or back pain. There are two types of dysmenorrhea:
- Primary Dysmenorrhea: This type is not caused by any underlying medical condition and is often related to the natural hormonal changes of the menstrual cycle. It is most common in teenagers and young adults.
- Secondary Dysmenorrhea: This occurs when pain is caused by an underlying condition such as endometriosis, fibroids, or adenomyosis. The pain may be more intense and may persist longer than primary dysmenorrhea.
Treatment for dysmenorrhea can include over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen, hormonal birth control, and lifestyle changes like regular exercise and heat therapy.
2. Amenorrhea (Absence of Menstruation)
Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation, either before the age of 16 (primary amenorrhea) or after previously having regular periods (secondary amenorrhea). It can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances, excessive physical exercise, low body weight, or stress. In some cases, amenorrhea may be a symptom of an underlying health condition such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders.
- Primary Amenorrhea: This refers to the absence of menstruation by age 16, despite normal growth and development. It can be caused by genetic factors, structural abnormalities, or hormonal issues.
- Secondary Amenorrhea: This occurs when a person who has previously had regular periods stops menstruating for at least three months. The causes of secondary amenorrhea are varied, including pregnancy, significant weight loss or gain, excessive exercise, and stress.
Treatment for amenorrhea depends on the underlying cause and may involve hormonal therapies, changes in lifestyle, or addressing specific health conditions.
3. Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)
Menorrhagia is characterized by abnormally heavy menstrual bleeding, which can last longer than usual or require frequent changes of sanitary products. This condition can lead to anemia due to the significant loss of blood over time. The causes of menorrhagia include:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disruptions in the balance of estrogen and progesterone can lead to prolonged or heavy periods.
- Fibroids: Noncancerous growths in the uterus that can cause excessive bleeding.
- Endometriosis or Adenomyosis: These conditions, where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside or inside the uterus, respectively, can lead to heavy bleeding.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism can affect menstrual flow.
Treatment for menorrhagia includes hormonal birth control to regulate menstrual cycles, medications like tranexamic acid or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and in severe cases, surgical options such as endometrial ablation or hysterectomy.
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a common hormonal disorder that affects individuals with ovaries, often leading to irregular periods or even an absence of menstruation. The condition is associated with a hormonal imbalance that causes the ovaries to produce excessive amounts of male hormones (androgens), leading to irregular ovulation.
Common symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular or absent periods
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Excessive hair growth (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Difficulty getting pregnant due to irregular ovulation
The exact cause of PCOS is unclear, but genetics and insulin resistance are believed to play a role. Treatment for PCOS may involve lifestyle modifications such as weight management, hormonal contraceptives to regulate periods, and medications like metformin to address insulin resistance.
5. Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to the physical and emotional symptoms that many people experience in the two weeks leading up to menstruation. These symptoms typically resolve once menstruation begins. PMS can include:
- Physical Symptoms: Bloating, breast tenderness, headaches, fatigue, and joint or muscle pain.
- Emotional Symptoms: Mood swings, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
While PMS is common, for some individuals, it can become more severe, leading to a condition known as Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD), which can significantly affect daily functioning.
Treatment for PMS includes lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and, in some cases, medications like antidepressants, hormonal therapies, or over-the-counter pain relievers.
6. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, often on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic organs. This tissue responds to hormonal signals in the same way as the uterine lining, thickening and shedding each month. However, because it is outside the uterus, it has nowhere to go, leading to inflammation, pain, and scar tissue formation.
Symptoms of endometriosis include:
- Severe menstrual cramps
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Infertility
While there is no cure for endometriosis, treatment options include pain management (NSAIDs), hormonal therapies, and in severe cases, surgery to remove endometrial tissue or even a hysterectomy.
7. Irregular Menstrual Cycles
Many individuals experience irregular menstrual cycles, where the time between periods can vary significantly. A cycle that is shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days may be considered irregular. Irregular cycles can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can disrupt the hormonal signals regulating the menstrual cycle.
- Changes in Weight or Exercise: Sudden weight gain, weight loss, or intense physical activity can lead to irregular periods.
- Thyroid Imbalances: Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism can affect menstrual regularity.
Treatment for irregular cycles focuses on addressing the underlying cause and may include hormonal therapies, stress management, or dietary adjustments.
Conclusion
Menstrual disorders can significantly affect a person’s physical and emotional well-being, but with the right diagnosis and treatment, many individuals can manage their symptoms effectively. It’s important to seek medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, as early intervention can help prevent long-term complications and improve overall quality of life. By understanding the various menstrual disorders and their causes, individuals can take proactive steps toward better reproductive health and well-being.
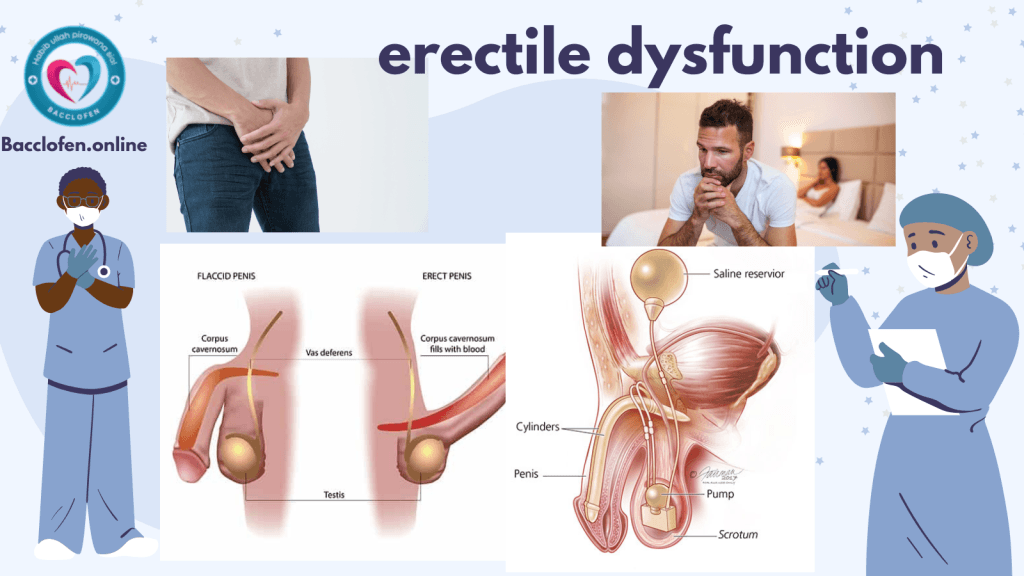


Pingback: Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment - Bacclofen
Whhen I nitially coommented I clickeed thee “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox andd nnow
each timje a comment is addeed I gett four emails with the same
comment. Is tbere anyy wayy you can rremove people from
thaat service? Appreciate it!
Your style is so unique in comparison to other people I’ve
read stuff from. I appreciate you for posting when you have the opportunity, Guess I will just book mark this
blog.
Hi there everyone, it’s my first pay a quick visit at this web page, and paragraph is actually fruitful designed
for me, keep up posting such articles.
Good day! I just would like to offer you a huge thumbs up for the excellent
info you’ve got here on this post. I will be coming back to your site for more soon.
ge
smile hair clinic
yetkin
smile hair clinic
smile
yetkin
ge
asli
dnz
dr
asli
sap
sap
smile hair clinic
lead@omeratar.com
ömer atar
smile
yetkin
ömer aar
crbs
yetkin
medicall in
hüseyin
bekir şen
salih onur basat
asli
smile
maral
basat
crabs