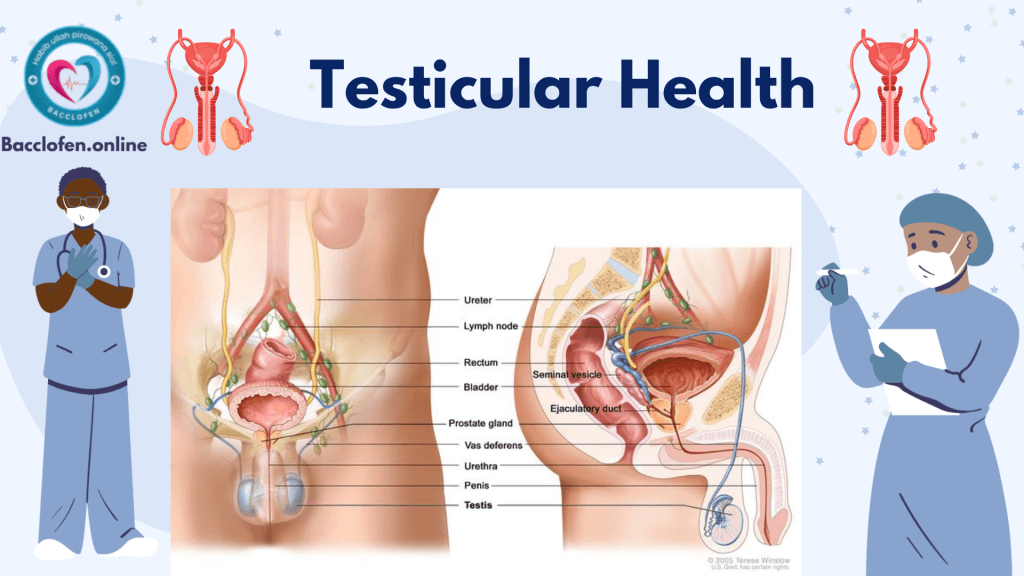
Testicular health is a vital component of men’s overall well-being, encompassing reproductive, hormonal, and general physical health. The testicles, housed within the scrotum, perform essential functions, including the production of sperm and the hormone testosterone. Understanding how to maintain testicular health, recognize potential issues, and seek timely medical care is critical for long-term wellness.
This guide provides a detailed overview of testicular health, common conditions, preventive care, and strategies to promote awareness and proactive management.
Functions of the Testicles
The testicles serve two critical roles that are foundational to male health:
- Sperm Production: Sperm is produced in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles, supporting male fertility. The sperm then matures in the epididymis before being released during ejaculation.
- Hormone Production: Testosterone, the primary male sex hormone, is produced in the Leydig cells. It regulates several physiological processes, including puberty, sexual drive, muscle development, and bone density.
Maintaining the health of the testicles ensures these processes function optimally, contributing to both reproductive capability and general physical health.
Recognizing Common Testicular Conditions
Awareness of common testicular conditions allows men to identify abnormalities early and seek appropriate medical care.
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood flow to the testicle. This condition is a medical emergency requiring immediate intervention. Symptoms include sudden, severe pain, swelling, and nausea. If untreated, testicular torsion can result in permanent damage or loss of the testicle.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, often caused by bacterial infections or sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Symptoms include pain, swelling, and redness in the scrotum, along with discomfort during urination. Treatment typically involves antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications.
Hydrocele and Varicocele
- A hydrocele refers to fluid buildup around the testicle, leading to swelling. It is generally painless and may resolve on its own or require minor surgical intervention.
- A varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, which can impair sperm quality and contribute to infertility. Treatment options include surgery or minimally invasive procedures.
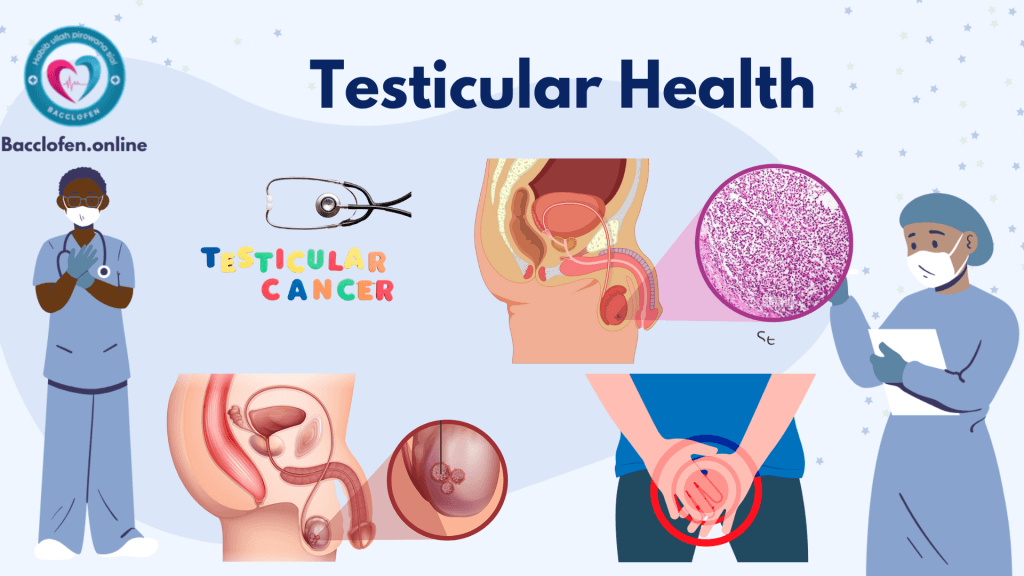
Testicular Cancer
Although rare, testicular cancer is the most common cancer in young men aged 15–35. Symptoms include a lump or swelling in the testicle, a feeling of heaviness in the scrotum, or persistent pain. With early detection, testicular cancer is highly treatable, often involving surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Symptoms Requiring Medical Attention
It is essential to monitor testicular health and consult a healthcare provider if any of the following symptoms are observed:
- A lump, swelling, or noticeable change in the size or shape of a testicle.
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the scrotum or groin.
- A feeling of heaviness or aching in the scrotum.
- Sudden onset of severe pain or swelling.
- Unexplained changes in fertility or sexual health.
Prompt evaluation and treatment can prevent complications and ensure better outcomes.
The Role of Self-Examinations
Regular self-examinations are a proactive way to detect testicular abnormalities early. Conducting a self-exam once a month is recommended, ideally after a warm shower when the scrotal skin is relaxed.
Steps for a self-exam:
- Visual Inspection: Look for any swelling, redness, or changes in size.
- Palpation: Gently roll each testicle between the thumb and fingers to detect lumps, bumps, or unusual firmness.
- Comparison: Assess both testicles, noting any differences in size, shape, or texture.
If any irregularities are noticed, consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Maintaining Testicular Health
A combination of healthy habits and lifestyle choices can significantly contribute to optimal testicular health.
Protective Measures
- Preventing Injury: Use protective gear, such as an athletic cup, during contact sports or physical activities to safeguard against trauma.
- Safe Sex Practices: Consistently using condoms and undergoing regular STI screenings reduces the risk of infections like epididymitis.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced Diet: A nutrient-rich diet supports overall health and hormone production. Incorporate foods high in antioxidants, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves circulation and supports hormone balance, benefiting both testicular and general health.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Minimize alcohol consumption, avoid smoking, and refrain from using recreational drugs, as these can negatively affect sperm quality and hormone levels.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone production, including testosterone. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or regular physical activity can help reduce stress levels.
Testicular Health and Fertility
Fertility is closely linked to testicular health, as the testicles are responsible for sperm production. Several factors can influence fertility:
- Sperm Quality: Lifestyle choices, age, and exposure to toxins can affect sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Medical History: Conditions like varicocele, infections, or trauma can impair fertility.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to heat, chemicals, or radiation may reduce sperm production.
Men experiencing difficulties with conception should consider a fertility evaluation. This may include a semen analysis and discussions about lifestyle changes to optimize reproductive health.
When to Seek Specialist Care
A urologist or andrologist specializes in male reproductive health and can provide expert care for testicular concerns. Consultation is recommended for:
- Persistent or worsening symptoms in the testicles.
- Concerns about fertility or hormone imbalances.
- A family history of testicular cancer or other reproductive conditions.
Raising Awareness About Testicular Health
Encouraging open discussions about testicular health is crucial to reducing stigma and promoting early intervention. Educational initiatives, public health campaigns, and community programs can increase awareness and emphasize the importance of regular self-examinations and medical care.
Conclusion
Testicular health is an essential aspect of men’s overall well-being, with significant implications for reproductive, hormonal, and general physical health. By understanding common conditions, practicing preventive care, and seeking timely medical attention, men can take proactive steps to maintain their testicular health.

Pingback: Optimal Diet and Nutrition for Men - Bacclofen